In securities trading, the term broker-dealer refers to individuals or firms that facilitate the buying and selling of securities. The “broker” half of the term refers to when firms act as agents for clients. The “dealer” role encompasses those times when firms act on their own behalf as principals in transactions. Broker-dealers include firms that
What is series
“What Is” Corporate Governance?
Corporate governance is defined as the framework of rules that provide direction for a company’s business functions. These guidelines helped executives, board members and other managers run a company in order to achieve its long-term goals and manage crises. Ultimately, corporate governance is intended to add value to a company while benefitting the company’s stakeholders.
What is series
“What Is” Direct Market Access (DMA)?
In global securities trading, the term direct market access (DMA) refers to the complex of networking, routing and software facilities that allow buy- side firms to cost-effectively execute transactions via regional and global trading venues. DMA services enable buy-side firms to send orders to exchanges and other trading venues via the memberships and trading infrastructure
What is series
“What Is” ISDA?
The International Swaps and Derivatives Association, a.k.a. ISDA, was established in 1985 by those in the privately negotiated, over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives trading markets. ISDA wants to achieve three mains goals: reduce counterparty credit risk, increase market transparency and improve the industry’s operational infrastructure. ISDA’s work covers derivatives based upon interest rates, credit, equity, FX, energy,
What is series
“What Is” Operational Risk?
Operational risk is classified as a form of loss caused by a company’s internal processes, which can be failures in a financial services company’s systems and people. In addition, operational risk can include legal actions or environmental events that serve as potential threats to a firm’s survival. Unlike market risk, operational risk is caused by
What is series
“What Is” an Exchange?
A key component of financial services is the buying and selling of investment instruments—chief among them is the trading of equity also known as stocks. The meeting place for buyers and sellers is an exchange, defined as a marketplace for trading a wide variety of financial instruments. The function of an exchange is to allow
What is series
“What Is” Performance Measurement?
Performance measurement is the process by which investors and others collect and examine information about financial services firms and their capabilities to make a profit. In general, the performance measurement department of a financial services firm such as a hedge fund or an asset manager is responsible for aggregating investment data and producing reports about
Dodd-Frank
“What is” a Hedge Fund
A hedge fund is a private partnership investment fund that uses complex investment strategies with the goal of maximizing returns on the funds’ underlying investments. Accredited investors run hedge funds and pool money in order to make risky, yet profitable investments. Therefore, despite the fact that “hedging” implies risk reduction, hedge funds tend to be
Fun Friday
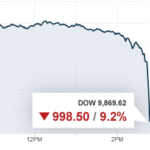
“What Is” The Flash Crash?
The Flash Crash, which happened after 2:30 pm EST on May 6, 2010, was a sudden, massive drop and recovery in securities prices. During the crash, the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell by nearly 1,000 points and bounced back within 20 minutes. The Flash Crash ranks as the biggest one-day, point decline in the Dow’s
What is series
“What Is” the Buy-Side?
In short, the buy side consists of firms looking to purchase assets or securities from the sell side, which offers these assets and other investment opportunities. The buy side mostly refers to the major institutions such as pension funds and insurance companies that are focused on maximizing the financial assets of their investors via purchases